/What is Edge Computing?


The development of edge computing technology has revolutionized the way we think about data processing and storage. With the growing demand for faster and more efficient access to data and applications, edge computing has emerged as a savior of sorts. In this article, we will explore the concept of this technology in the context of servers, including its definition, history and applications. We will also discuss the features, advantages and disadvantages of this solution in servers and the latest trends and technologies in this field.
Edge Computing. What is it?
Edge computing is a distributed processing model that brings data processing and storage closer to where it is needed to reduce latency and increase efficiency. This concept was first introduced in 2014 and has since gained popularity due to the growth of the Internet of Things (IoT) and the need for real-time data processing.
History behind it
Its origins can be traced to the concept of distributed computing, which dates back to the 1970s. However, the specific term "edge computing" was coined in 2014 by Cisco, which recognized the need for a new computing model to handle the growing number of IoT devices.
How does it work?
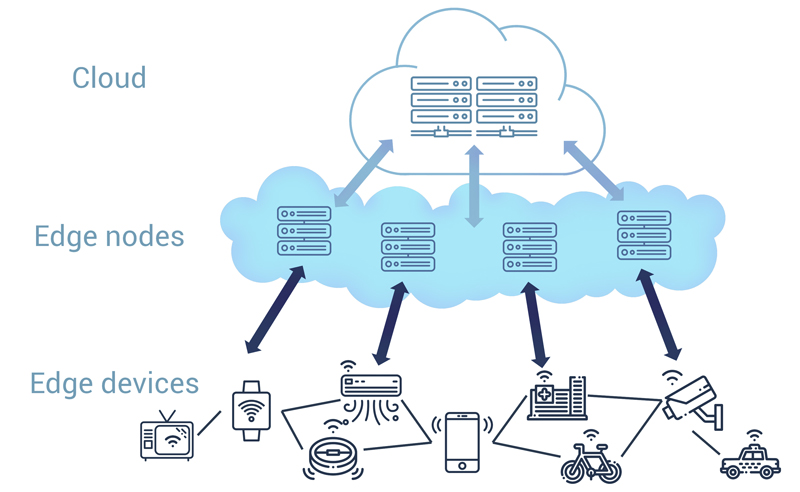
Edge computing involves deploying small low-powered computers, known as edge devices, at the edge of the network, closer to where the data is generated. These edge devices process and store data locally, and send only the most relevant data to the cloud for further processing and storage. This reduces the amount of data that must be sent to the cloud, thereby reducing latency and improving response time.
Edge computing in the context of servers
Edge computing is increasingly being applied to servers, especially in the context of edge data centers. Edge data centers are smaller data centers that are located closer to end users to provide faster access to data and applications. By deploying edge servers in these locations, enterprises can improve the performance of their applications and reduce latency.
Server aiming features
Edge computing in servers offers a number of key features, including:
- Low latency – processing data locally, edge servers can provide users with real-time responses.
- Scalability – edge servers can be easily scaled up or down as needed, allowing companies to respond quickly to changes in demand.
- Safety – by processing data locally, edge computing helps improve data security and privacy, as sensitive data does not need to be transmitted over the network.
- Cost effectiveness – by reducing the amount of data that must be sent to the cloud, edge computing can help reduce the cost of cloud storage and processing.

Advantages of edge computing in servers
Edge computing in servers offers a number of benefits to enterprises, including:
- Improving performance – By reducing latency and improving response time, edge computing can help companies deliver faster and more responsive applications.
- Improved reliability – Processing data locally, edge servers can help ensure that applications remain operational even if connectivity to the cloud is lost.
- Greater flexibility – By deploying edge servers, companies can choose to process data locally or in the cloud, depending on their specific needs.
- Enhanced security – By processing data locally, edge computing can help improve data security and privacy.
Disadvantages of edge computing in servers
While edge computing in servers offers many benefits, there are also some potential drawbacks to consider. These include:
- Increased complexity – Deploying edge servers requires careful planning and management, and can add complexity to the overall IT infrastructure.
- Higher costs – Deploying edge computing can be more expensive than relying solely on cloud infrastructure, due to the need to purchase and maintain additional hardware.
- Limited processing power – Edge servers may have limited processing power compared to cloud servers, which may affect their ability to handle large amounts of data.
Summary
Edge computing is a powerful technology that can help businesses improve the performance, reliability and security of their applications. By deploying edge servers, companies can enjoy the benefits of edge computing while taking advantage of the scalability and cost-effectiveness of cloud computing. However, it is important to carefully consider the potential advantages and disadvantages of edge computing before deciding to implement it.








